Preface
Even casual Friday surveys may have some educational value. Since we "already know" that Java "needs more than 32 GB of RAM", the questions arise: how to monitor memory consumption for applications written in Java? How to check the performance of a Java application under heavy load? These questions are answered in the bonus section. In two Friday surveys, I asked the following questions: How much RAM do you need to code in Java? and How many monitors do you need to code in Java?. Thank you all for your answers and participation in the survey!
Overview of surveys
Both the amount of RAM and the number of monitors are very important elements when it comes to the comfort of work of a programmer. In terms of RAM, it's not that Java needs a lot of RAM, but that all the necessary development tools combined together result in a high RAM requirement. Several additional monitors allow you to use multiple development tools at the same time.
How many monitors do you need to code in Java?

Survey result
It can be seen that the ideal combination in terms of the number of monitors is one monitor from the laptop plus an additional monitor on the desk - 46% of people answered so. I haven't worked in such a configuration myself. I only used a laptop (25% of votes) or two external monitors and a laptop (21% of votes). It seems that 1/2 of people use a laptop plus an additional monitor. However, approximately 1/4 of people use only a laptop and/or a laptop plus two additional monitors.
Why have more than one monitor?
When programming, you can write the application source code on one monitor, check the logs of the running application on the other, and browse the application's website and/or search for information on the Internet on another.
Monitor examples – Midjourney AI
Poniżej przykładowy zestaw dwóch monitorów oraz jeden długi monitor z zakrzywionym wyświetlaczem. Mój prompt: /imagine two monitors desktop set oraz /imagine long curved monitor desktop set.


Ile pamięci RAM potrzeba do kodowania w języku Java?

Survey result
To write code in Java you need 32 GB of RAM, and even more - 43% of people answered yes. I can guess what the people who voted wanted to say. The development environment and toolkit as a whole requires a lot of RAM. I once tried to program on a laptop with 8 GB RAM, but I quickly ended up replacing the laptop with one with 32 GB RAM. Some people - 20% - program with 8 GB RAM, and another group of people - 26% - need 16 GB RAM.
Why a minimum of 16 GB of RAM?
As I mentioned above, I quickly had to switch from 8 GB to 32 GB of RAM. Why? For programming in "pure Java", plus an IDE, e.g. IntelliJ IDEA, 8GB of RAM is enough. Pure Java alone is not enough, programmers also need an application server, a database + a graphical application to support it, and some containerization mechanism, e.g. Docker.
IntelliJ IDEA itself, "when it gets up to speed", can use 2 GB of RAM. That's why developers are looking for "lightweight" application and database servers. What do I mean by "light"? It is one that uses little RAM, consumes few operating system resources and takes up little disk space.
Spring Boot uses a built-in Tomcat server and supports the built-in H2Database database, this was one of the elements that allowed the Spring Framework to become so popular. I wrote more about it in my article We use "old" frameworks - Java EE vs. Spring Framework – David vs. Goliath.
Comparison of server demand for RAM
Application servers:
- Apache Tomcat – 512 MB RAM.
- WildFly (formerly JBoss) - from 2-4 GB to 8 GB of RAM.
Database servers:
- H2Database – 2 MB RAM.
- Oracle Database - from 4 GB to 16 GB.
I realize that the above comparison concerns different classes of servers for different applications, but I want to show how different the demand for system resources, such as RAM, can be.
Summary of server differences - ChatGPT AI
Prompts I used: "Compare system requirements for servers: Tomcat and Wildfly" and "Compare system requirements for Oracle Database and H2Database".
Application servers
In summary, Tomcat is a lightweight and flexible servlet container, suitable for a wide range of applications with modest system requirements. WildFly is a more comprehensive Java EE application server designed for enterprise-grade applications, and it requires higher system resources to operate efficiently. Your choice between the two should depend on the specific needs and scale of your application.
Database servers
In summary, Oracle Database is a heavyweight, enterprise-grade database system with high system requirements, designed for large-scale and mission-critical applications. H2 Database, on the other hand, is a lightweight, embeddable database system with modest system requirements, making it suitable for smaller projects, prototyping, and embedded scenarios. The choice between the two should depend on your specific use case and the resources available for your database system.
BONUS: Java application performance – monitoring and testing
Although Java itself does not consume a large amount of RAM, applications written by us can consume huge amounts of it due to, for example: memory leaks. In this case, the first issue is to monitor the resources used by Java applications. The second issue is how to safely load Java applications to such an extent that performance problems occur. The following tools come to our aid: JConsole and JMeter.
Monitoring resources and performance of Java applications - JConsole
JConsole is part of the Java Development Kit (JDK) and the graphical console can be launched using the "jconsole" command. It can be used to obtain information about the performance and resource consumption of applications running on the Java platform.
JConsole
The JConsole graphical user interface is a monitoring tool that complies to the Java Management Extensions (JMX) specification. JConsole uses the extensive instrumentation of the Java Virtual Machine (Java VM) to provide information about the performance and resource consumption of applications running on the Java platform. Źródło: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/management/jconsole.html
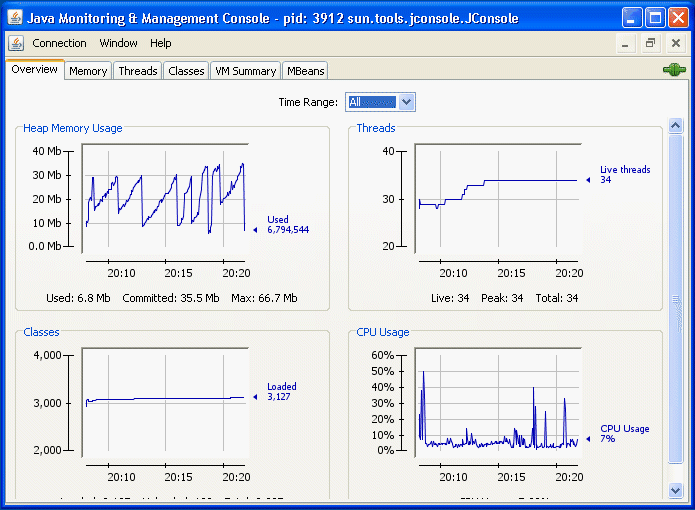
The Overview tab displays graphical monitoring information about CPU usage, memory usage, number of threads, and classes loaded into the Java VM, all on one screen.
Load testing and performance monitoring of Java applications - JMeter
JMeter is used as a load testing tool to analyze and measure the performance of various services, with a focus on web applications.
JMeter
The Apache JMeter™ application is open source software, a 100% pure Java application designed to load test functional behavior and measure performance. It was originally designed for testing Web Applications but has since expanded to other test functions. Źródło: https://jmeter.apache.org/

It can be used to verify the performance of "pure Java classes" using "Java Request".
Java Request – JMeter
This sampler lets you control a java class that implements the org.apache.jmeter.protocol.java.sampler.JavaSamplerClient interface. By writing your own implementation of this interface, you can use JMeter to harness multiple threads, input parameter control, and data collection. Źródło: https://jmeter.apache.org/usermanual/component_reference.html#Java_Request
You can also use JMeter to verify the performance of unit tests written in JUnit using the "JUnit Sampler". Source https://jmeter.apache.org/usermanual/junitsampler_tutorial.html
Summary
As I wrote at the beginning, even casual Friday surveys may have some educational value. When discussing the amount of RAM needed to write Java applications, we learned that Java itself does not actually use that much RAM. This is a programming environment, i.e. tools and servers need a lot of RAM. Answering the question about the number of monitors needed, we learned that when programming, you can write the application's source code on one monitor, check the logs of the running application on the other, and browse the application's website and/or search for information on the Internet on the next. Finally, I showed useful resources and performance monitoring tools - JConsole - and a load testing and performance monitoring tool - JMeter - both tools for applications written in Java.